How Asset Tracking Technology Can Streamline Business
Estimated Reading Time
5 minutes
What is Asset Tracking?
Asset tracking is an umbrella term that describes keeping track of the location and important details of materials of interest. These materials can be anything – from nuts and bolts, to tools, to finished products, and even entire vehicles. In brief, asset tracking is keeping track of what is where, and when. Unsurprisingly, this is very important for a business to know for reasons ranging from inventory stock keeping to product delivery verification and everywhere in between.
Historically done on paper within ledgers and methodically updated as materials moved from one location to another, asset tracking has evolved in the modern day to become increasingly automated with the help of IoT technology. Thanks to the advent of the internet in conjunction with various localization technologies such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), and Global Positioning Systems (GPS), keeping a close eye on assets has become easier and more accurate than ever before.
Asset tracking is an umbrella term that describes keeping track of the location and important details of materials of interest.
Charles Modrich
Senior Hardware Engineer – TeraCode
What is RFID?
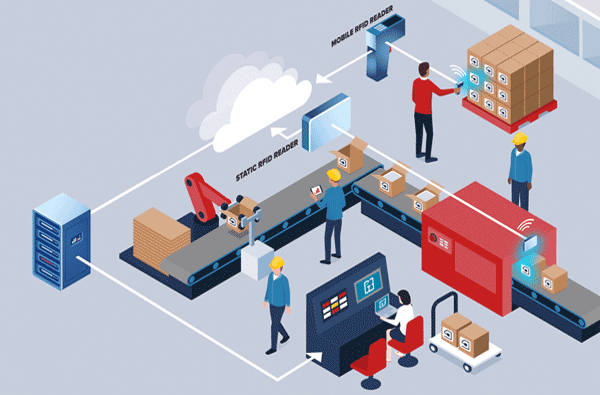 RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that affixes small paper tags with an embedded microchip and antenna on to materials of interest. These microchips can be programmed with many aspects that can be used to describe a material: what it is, where it’s going, who it’s going to/from, and so on. These chips are read using RFID readers that can wirelessly power and read these microchips to pull the information from each one. RFID readers can be hand-held by workers to scan individual items similar to a bar-code scanner, or be larger more powerful stationary units that can scan many RFID tags from a distance such as items passing through a conveyor belt system.
RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that affixes small paper tags with an embedded microchip and antenna on to materials of interest. These microchips can be programmed with many aspects that can be used to describe a material: what it is, where it’s going, who it’s going to/from, and so on. These chips are read using RFID readers that can wirelessly power and read these microchips to pull the information from each one. RFID readers can be hand-held by workers to scan individual items similar to a bar-code scanner, or be larger more powerful stationary units that can scan many RFID tags from a distance such as items passing through a conveyor belt system.
The information from these readers is then usually automatically uploaded to the cloud for storage and manipulation within the business’ systems. Location information is dependent on the location of the RFID reader reading the tags, so by knowing what reader is scanning which tags, the tags themselves can be “checked off” as being present at that reader location, at that specific time.
Localization
Discontinuous, line of sight
Tracker Connectivity
Directly via ethernet, WiFi, or cellular, indirectly via LPWAN
What are the advantages of RFID?
Extremely inexpensive per-unit tagging for just a few cents per tag, whereby a business can tag and track thousands of items relatively inexpensively.
What are the disadvantages of RFID?
Tags must pass directly beneath the scanning region of a reader – very short distances for handheld, less short but often still direct distances for static readers meaning these readers must be positioned with forethought and care.
Assets are only known to the system at read time, and not elsewise – if an asset is being moved from point A to point B, is scanned at point A but goes missing along the way and is never scanned at point B, the asset can be lost. RFID scanners are relatively expensive, even if the tags are not.
Use cases of RFID
Warehouse inventory management, material shipping/receiving (both within a large company, and company to company), manufacturing line quality assurance tracking, materials traceability for medical and military manufacturing.
What is BLE?
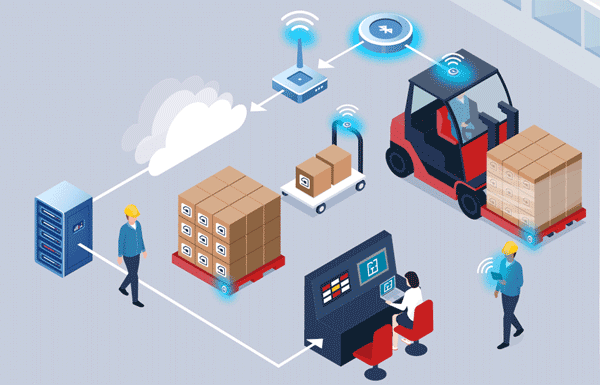 BLE or Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless technology that allows information to be transferred wirelessly between two BLEcapable devices. While most know of Bluetooth or BLE as a technology often used for shuttling audio to wireless speakers or headphones, it has many other use cases as well including asset tracking.
BLE or Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless technology that allows information to be transferred wirelessly between two BLEcapable devices. While most know of Bluetooth or BLE as a technology often used for shuttling audio to wireless speakers or headphones, it has many other use cases as well including asset tracking.
In the case of asset tracking, extremely small, battery-efficient BLE devices are fixed on to the materials of interest. These devices then periodically send out a radio frequency signal containing information about the asset, that is picked up by a nearby BLE-scanning device that forwards the received information to the cloud, as well as approximate location information relative to the BLE-scanning device that can be used to more accurately locate the asset.
Once information about an asset is received by a BLE-scanner, the information must be relayed to the cloud via WiFi or LPWAN to a cable or cellular uplink.
Localization
Continuous, within a room or building
Connectivity
Directly via ethernet, WiFi, or cellular, indirectly via LPWAN asset tracking IoT solutions
What are the advantages of BLE?
Unlike RFID, BLE does not require line-of-site to the asset of interest. One BLE scanner can pick up and forward signals from hundreds of tagged assets within a large spherical area, and can localize these assets even if they are moved within the region of interest even when out of sight of the scanner. Since BLE tags send a signal out periodically, so long as the signal is within range of the BLE scanner asset information can be updated in nearly real time as well. For small deployments with few assets to be tracked, BLE asset tracking is often cheaper than RFID due to the relatively low cost of BLE scanners compared to RFID readers. Also unlike RFID tags which often can only be written to once, BLE tags can be reused and re-written with new product information so long as the years-long battery lasts.
What are the disadvantages of BLE?
Unlike RFID tags that are powered wirelessly by an RFID reader at scan-time, BLE tags must be equipped with their own power supplies that will eventually run out, leaving the tag unusable. Due to this requirement BLE tags are also much more expensive than RFID tags, and thus become more suitable to asset tracking applications with fewer assets to be tracked.
Use cases of BLE
Agriculture, education, retail, hospitality, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, warehouse tracking. That is: Tool tracking, very important asset tracking, product tracking, batch tracking, pallet tracking.
What is GPS?
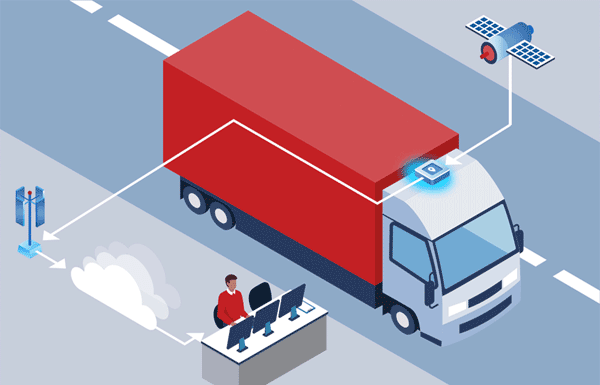 The most commonly known asset tracking technology, GPS or Global Positioning System is a satellite-based tracking system that leverages signals from many satellites in orbit to determine an approximate location of a GPS device on earth. GPS devices are accurate to within several meters and offer near real-time tracking of the asset of interest, but usually require open air to function with acceptable accuracy, and must be paired with a long range transmitter that enables a cellular, LPWAN, or Satellite connection to relay the GPS and asset information back home.
The most commonly known asset tracking technology, GPS or Global Positioning System is a satellite-based tracking system that leverages signals from many satellites in orbit to determine an approximate location of a GPS device on earth. GPS devices are accurate to within several meters and offer near real-time tracking of the asset of interest, but usually require open air to function with acceptable accuracy, and must be paired with a long range transmitter that enables a cellular, LPWAN, or Satellite connection to relay the GPS and asset information back home.
Localization
Continuous, global coverage
Tracker Connectivity
Directly via cellular, indirectly via LPWAN
What are the advantages of GPS?
Unlike RFID and BLE location tracking, GPS tracking does not rely on another external device to provide location information. Additionally, so long as satellites and internet connectivity are available, assets can be tracked over extremely long distances in nearly real time.
What are the disadvantages of GPS?
GPS devices are power hungry, necessitating large batteries or hard-lined power connections in order to function for long periods of time. Additionally, connectivity is often a concern for these devices due to their remote applications – requiring costly uplink methods such as cellular or satellite connectivity. Weather conditions and satellite availability also heavily affect the performance of these devices, potentially resulting in reduced localization accuracy at best, and spotty or no location information at worst.
Use cases of GPS
Large asset tracking: freight container tracking, vehicle tracking, pallet tracking.
Make IOT Easy
To learn more about how asset tracking technology can help your business, please get in touch.





 RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that affixes small paper tags with an embedded microchip and antenna on to materials of interest. These microchips can be programmed with many aspects that can be used to describe a material: what it is, where it’s going, who it’s going to/from, and so on. These chips are read using RFID readers that can wirelessly power and read these microchips to pull the information from each one. RFID readers can be hand-held by workers to scan individual items similar to a bar-code scanner, or be larger more powerful stationary units that can scan many RFID tags from a distance such as items passing through a conveyor belt system.
RFID or Radio Frequency Identification is a technology that affixes small paper tags with an embedded microchip and antenna on to materials of interest. These microchips can be programmed with many aspects that can be used to describe a material: what it is, where it’s going, who it’s going to/from, and so on. These chips are read using RFID readers that can wirelessly power and read these microchips to pull the information from each one. RFID readers can be hand-held by workers to scan individual items similar to a bar-code scanner, or be larger more powerful stationary units that can scan many RFID tags from a distance such as items passing through a conveyor belt system. BLE or Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless technology that allows information to be transferred wirelessly between two BLEcapable devices. While most know of Bluetooth or BLE as a technology often used for shuttling audio to wireless speakers or headphones, it has many other use cases as well including asset tracking.
BLE or Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless technology that allows information to be transferred wirelessly between two BLEcapable devices. While most know of Bluetooth or BLE as a technology often used for shuttling audio to wireless speakers or headphones, it has many other use cases as well including asset tracking. The most commonly known asset tracking technology, GPS or Global Positioning System is a satellite-based tracking system that leverages signals from many satellites in orbit to determine an approximate location of a GPS device on earth. GPS devices are accurate to within several meters and offer near real-time tracking of the asset of interest, but usually require open air to function with acceptable accuracy, and must be paired with a long range transmitter that enables a cellular, LPWAN, or Satellite connection to relay the GPS and asset information back home.
The most commonly known asset tracking technology, GPS or Global Positioning System is a satellite-based tracking system that leverages signals from many satellites in orbit to determine an approximate location of a GPS device on earth. GPS devices are accurate to within several meters and offer near real-time tracking of the asset of interest, but usually require open air to function with acceptable accuracy, and must be paired with a long range transmitter that enables a cellular, LPWAN, or Satellite connection to relay the GPS and asset information back home.





